|
| Performance |
Hs-126
with Bramo 232
engine |
Hs-126
with BMW-132Dc
engine |
| Wingspan, m |
14.50 |
| Length, m |
10.85 |
| Height, m |
4.30 |
| Wing area, m² |
31.6 |
| Empty weight, kg |
2,160 |
2,050 |
| Loaded weight, kg |
3220/32841 |
3150 |
| Power, hp/at altitude, m |
780 / 4300 |
790 / 2900 |
| Max speed at sea level, km/h |
307 |
- |
| Max speed, km/h / at altitude, m |
370 / 5,000 |
355 / 3000 |
| Cruise speed, km/h / at altitude, m |
314 / 4,000 |
300 / 3000 |
| Max diving speed, km/h |
480 |
480 |
| Landing speed, km/h |
90 |
95 |
| Time to level, min / at altitude, m |
11.7 / 6,000 |
13.5 / 6000 |
| Service seiling, m |
8,050 |
8,900 |
| Radius at cruise speed, km |
1,000 |
950 |
| Taking - off, m |
294 |
- |
| Run, m |
415 |
- |
1- In numerator - Reconnaissance aircraft; in a denominator - light bomber
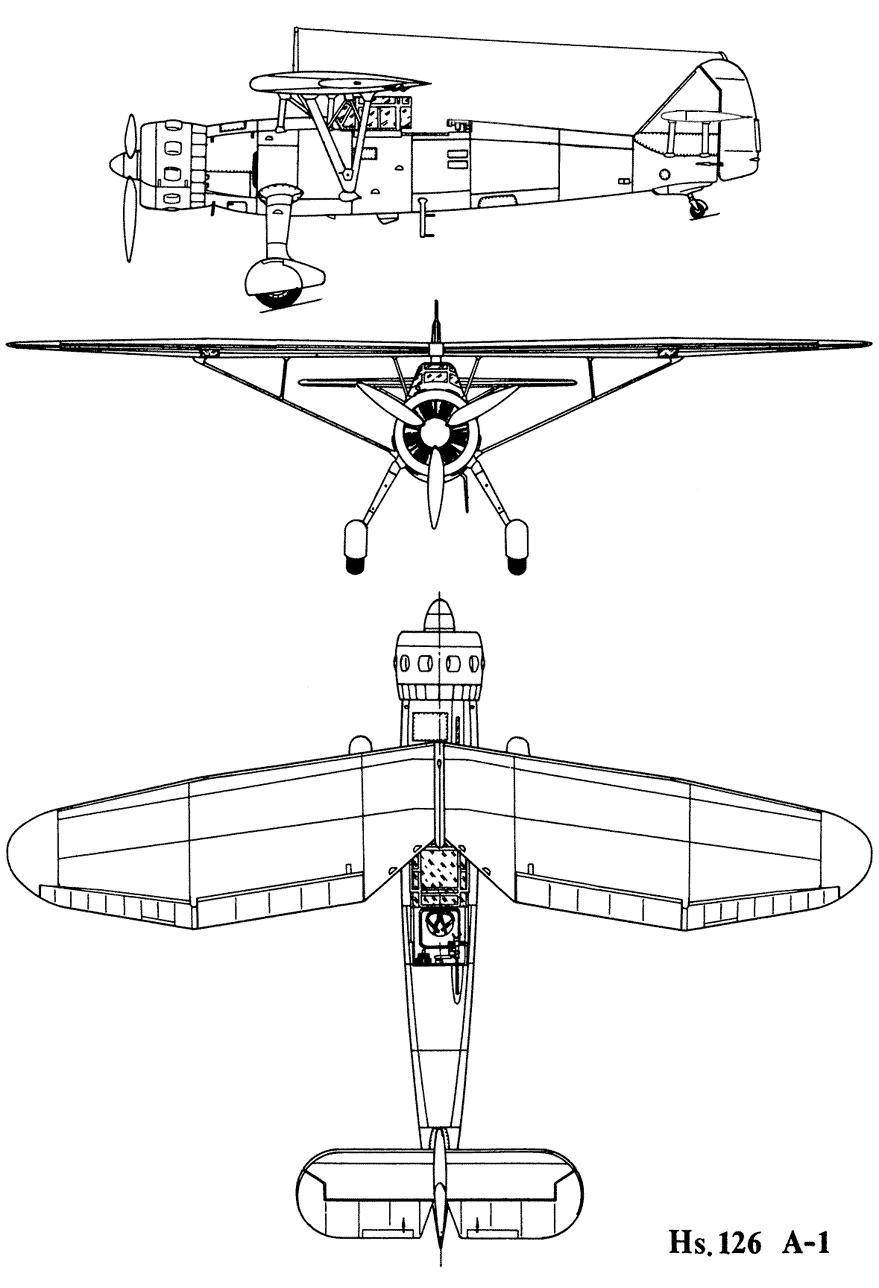 |
Drawing Hs.126A-1
|
 |
Henshel Hs-126
|
The aircraft could be successfully used as a tactical day and night close-range reconnaissance aircraft, an artillery fire spotter, a light bomber and an attack aircraft, perform communications missions and send saboteurs to the enemy's near rear. This concept of a universal machine for interaction with ground forces became widespread in the air forces of many countries before the start of the Second World War. One of its brightest representatives, for example, can be the English Lysander aircraft, which is similar in many respects (from the design scheme to the functions performed) to the Hs 126.
In July 1938, the first copies of the new aircraft began to enter the Luftwaffe close-range reconnaissance detachments to replace the outdated He 45 and He 46. The mastering of the Hs 126 by the flight crew proceeded smoothly and without serious problems - a simple and very reliable aircraft turned out to be quite accessible even to yesterday's graduates of German flight schools Air force. On September 20, 1938, the combat units had 42 Henschel reconnaissance aircraft (of which 35 were serviceable).
The combat debut of the 126th took place in the late autumn of 1938. Six copies of the A-1 modification were sent to Spain, where at that time there was a bloody Civil War. They joined Recon Squadron 5.AU88 of the Condor Legion to replace the He 45 and took part in the final phase of the conflict, successfully operating as reconnaissance aircraft and light bombers.
Bibliography

- "Aviation of Luftwaffe" /Viktor Shunkov/
- "Encyclopedia of military engineering" /Aerospace Publising/
|






