|
KL 106
 |
- Trainer aircraft
- First flight: 1937
- Klemm
|
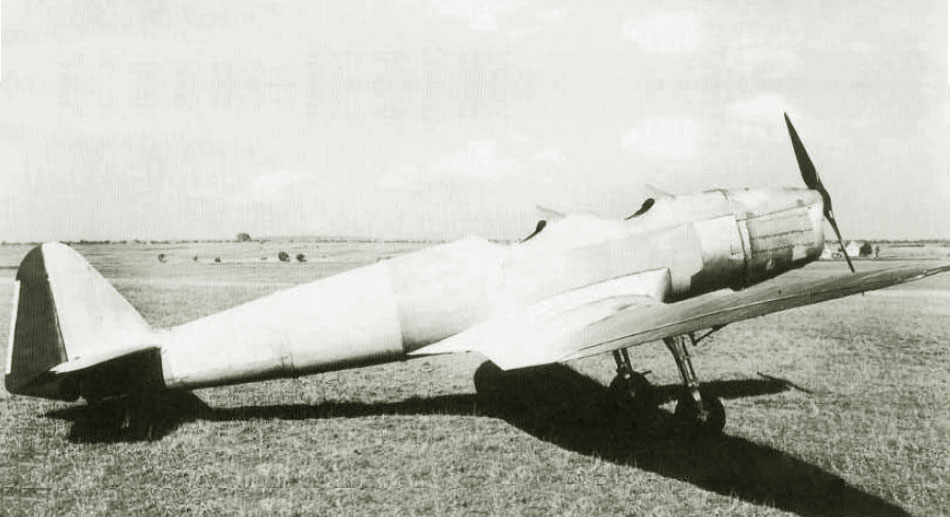
In 1937, the Leichtflugzeugbau Klemm developed a variant of the KL-35D aircraft, designated KL-106. The development of the aircraft was carried out by order of the American company Davis & Co., which planned to launch its production in the United States.
The first KL-106 V1 prototype (D-EBCQ, Werk-Nummer 1240) was equipped with a 65 hp Hirth HM 60 engine. Tests showed that the design was overweight. In the second prototype of the KL-106 V2 (Werk-Nummer 1241), the all-metal parts of the hull and wings were replaced with a structure made of metal pipes and wooden cladding.
The last aircraft with the HM 60 was the third prototype (D-EBCQ). Until June 1939, 7 more copies of the aircraft were made (V4 D-EPQG, V5 D-ECAH, V6 D-EQMR, V7 D-EDFK, V8 D-ERQS, V9 D-EECD and V10 D-ESHR) already with the Hirth engine HM 504 A 105 hp (77 kW.). These machines became the KL-106A-0 series aircraft.
In connection with the outbreak of World War II, not a single copy was delivered to the customer, and all KL-106s were distributed among members of the Nationalsozialistischen Fliegerkorps, some of them were used by the Luftwaffe as training aircraft.
|
| Crew |
2 |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Wing span, m |
11.20 |
| Wing area, m² |
14.50 |
| Height, m |
2.17 |
| Length, m |
8.10 |
| Powerplant |
|---|
| 1 × PE Hirth HM 504 A, power hp |
1 × 105 |
| Weights, kg |
|---|
| Empty weight |
495 |
| Gross weight |
780 |
| Performance |
|---|
| Maximum speed, km/h |
192 |
| Cruise speed, km/h |
180 |
| Rate of climb, m/min |
196 |
| Service ceiling, m |
4,700 |
| Service range, km |
780 |
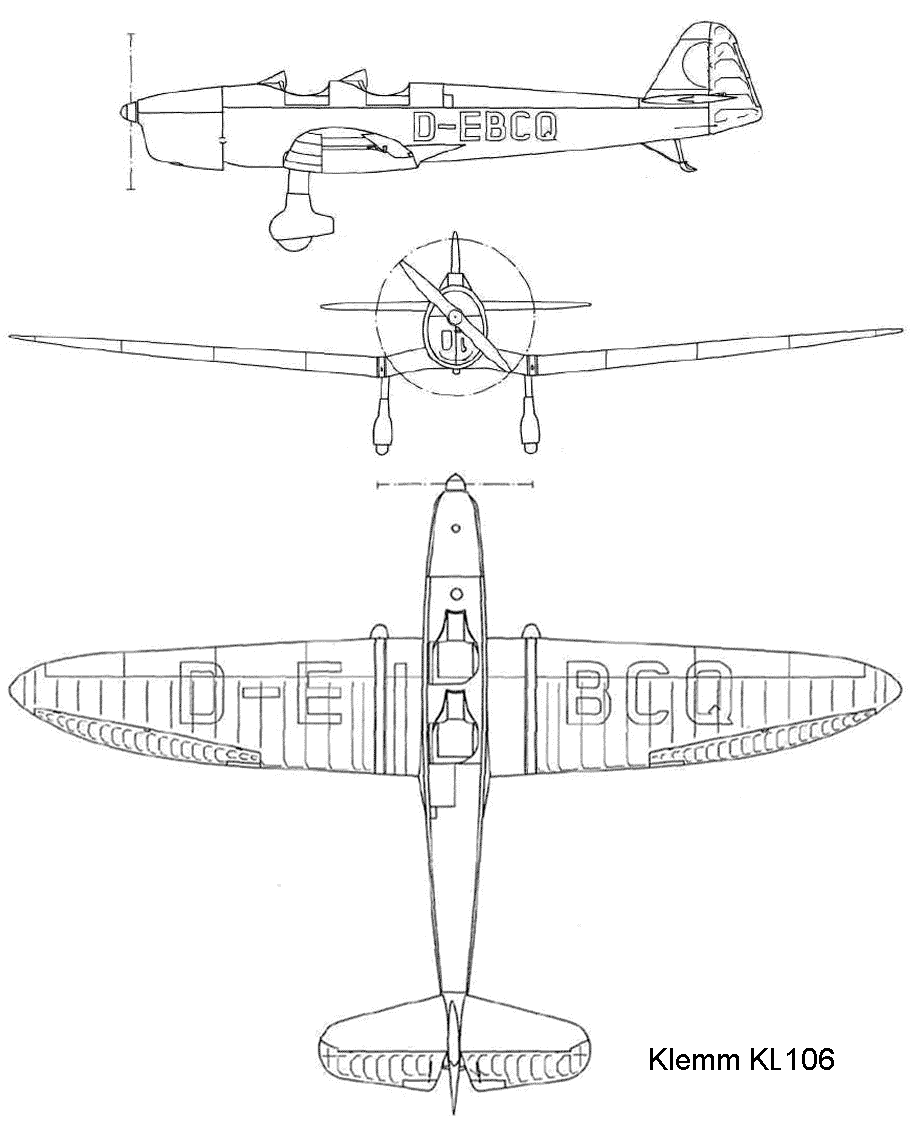 |
Drawing Kl 106 A-0
|
KL 107
 |
- Trainer aircraft
- First flight: 1939
- Klemm
|
The development of the Klemm KL-107 aircraft began by German aircraft manufacturers back in 1936, while the main goal set for the Klemm engineers was the need to create a multi-purpose aircraft suitable both for private use and for training future pilots, including military pilots .
A modified version of the KL-107, developed on the basis of the KL-105, also did not find support from the military. The first flight of the prototype took place in 1940, while, due to the actual start of the Second World War, the production of aircraft of this model was very limited - only 7 aircraft were built in the 40s.
However, after the end of the war, Bolkow revived the project by buying a license from Klemm for its release under the new designation В.107. The aircraft entered production in 1959 and was produced until 1966 inclusive in versions - KL-107B - the main production version of the aircraft, equipped with a 160 hp Lycoming O-320-A1A engine, KL-107C - an upgraded three-seat version aircraft and KL-107D - four-seater version.
The Klemm KL 107 aircraft has good aerodynamic shapes and is capable of flying at fairly high speeds, which is also mainly facilitated by the powerful Powerplant, represented by an 82 hp Hirth HM 60R aircraft engine, which is quite a bit. The maximum flight speed of this aircraft is 190 km / h, while the flight range is limited to a short distance of only 670 kilometers, which is far from always practical and efficient.
The cockpit of the aircraft has a sufficiently large amount of free space, which makes air travel very comfortable for both the passenger and the pilot. Transportation of goods on board the aircraft is not possible, since, first of all, there is a strict weight limit - the payload taken on board the aircraft is only 150 kilograms, and in addition, due to the compactness of the cabin, the placement of any cargo here is also impossible. However, the aircraft of this model until the 80s of the last century was very often used as a training aircraft, but later, the aircraft was used exclusively by private owners for their own purposes.
|
| Crew |
2 |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Wing span, m |
10.80 |
| Wing area, m² |
14.60 |
| Height, m |
2.15 |
| Length, m |
8.10 |
| Powerplant |
|---|
| 1 × PE Hirt HM 500, power hp |
1 × 100 |
| Weights, kg |
|---|
| Empty weight |
480 |
| Gross weight |
860 |
| Performance |
|---|
| Maximum speed, km/h |
190 |
| Cruise speed, km/h |
180 |
| Rate of climb, m/min |
176 |
| Service ceiling, m |
4,200 |
| Service range, km |
670 |
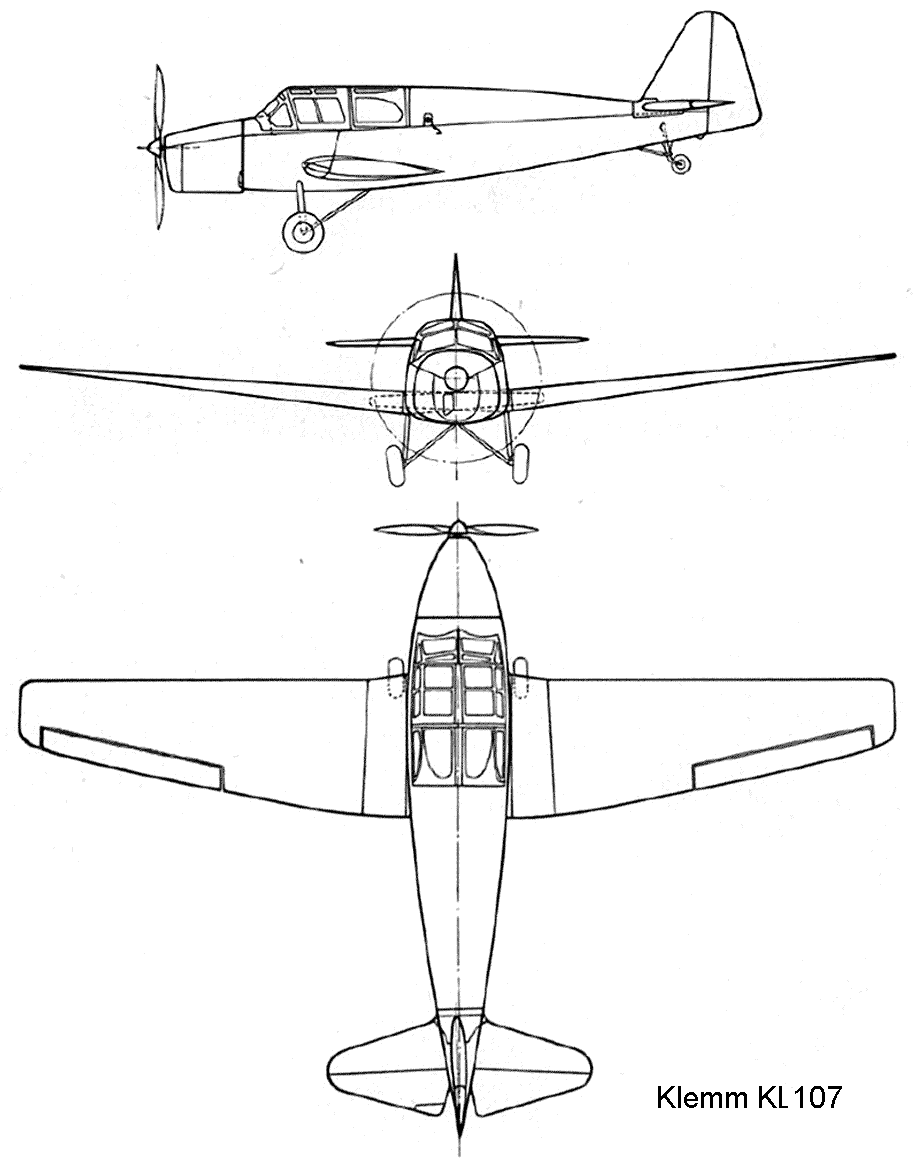 |
Drawing KL 107
|
KL 151
 |
- Multipurpose auxiliary aircraft
- First flight: 1942
- Klemm
|
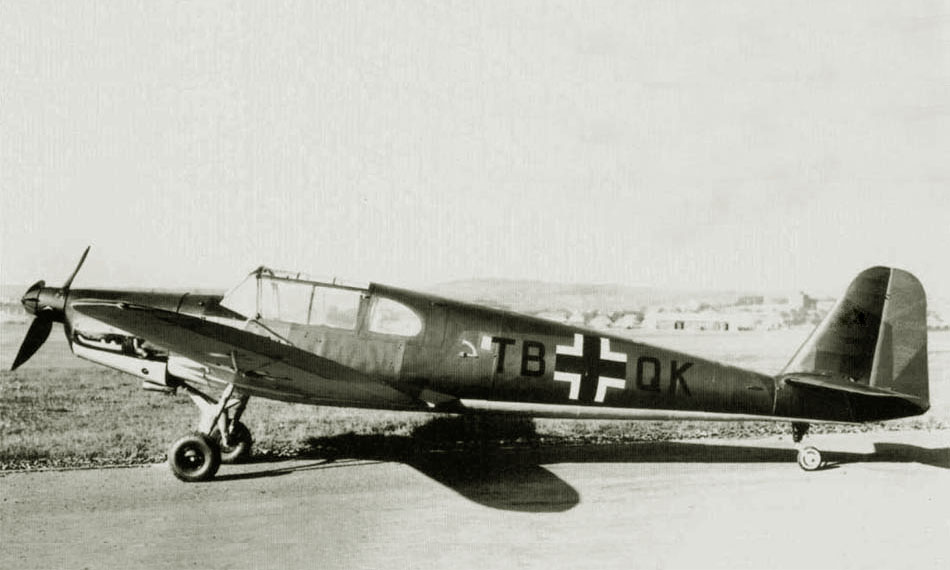
In 1940, the German Imperial Aviation Ministry (Reichsluftfahrtministerium - RLM) asked the Leichtflugzeugbau Klemm firm to develop an aircraft capable of replacing the outdated Bf.108. The main requirement was the saving of aluminum in the construction of the aircraft. To speed up the work, the designers of the company took the fuselage and wings from the KL-107 trainer as a basis.
As a result, the first prototype of the KL-151 V1 (TB + QK) aircraft took off on September 10, 1942. It was a four-seat wooden low wing powered by a 177 kW (240 hp) eight-cylinder Argus As 10 P V-twin engine.
Only on February 19, 1943, the aircraft entered the disposal of the DVL (Deutsche Versuchsanstalt für Luftfahrt). Already during the tests, the requirements for the aircraft were replenished, now much attention was paid to increasing the reliability of the retractable landing gear. The KL-151 V-1 was returned to the factory, where the aircraft was used as Hans Klemm's personal transport. In July 1944, the prototype was destroyed by Allied bombing.
The finalization of the V2 variant was transferred to the Czech plant Zlin, where the designers coped with the problem of increasing the reliability of the chassis. But until the end of the war, not a single copy of the aircraft was completely completed. The KL-105B-1 variant with a twelve-cylinder Argus As 410 engine with an HP 350 power remained on paper. (261 kW).
After the end of the war, Klemm planned to revive the project, but in the end he chose the KL-107.
|
| Crew |
2 |
| Dimensions |
|---|
| Wing span, m |
12.40 |
| Wing area, m² |
20.80 |
| Length, m |
9.17 |
| Powerplant |
|---|
| 1 × PE Argus As 10 P, power hp |
1 × 240 |
| Weights, kg |
|---|
| Empty weight |
800 |
| Gross weight |
1500 |
| Performance |
|---|
| Maximum speed, km/h |
238 |
| Cruise speed, km/h |
215 |
| Service ceiling, m |
5,800 |
| Service range, km |
1,200 |
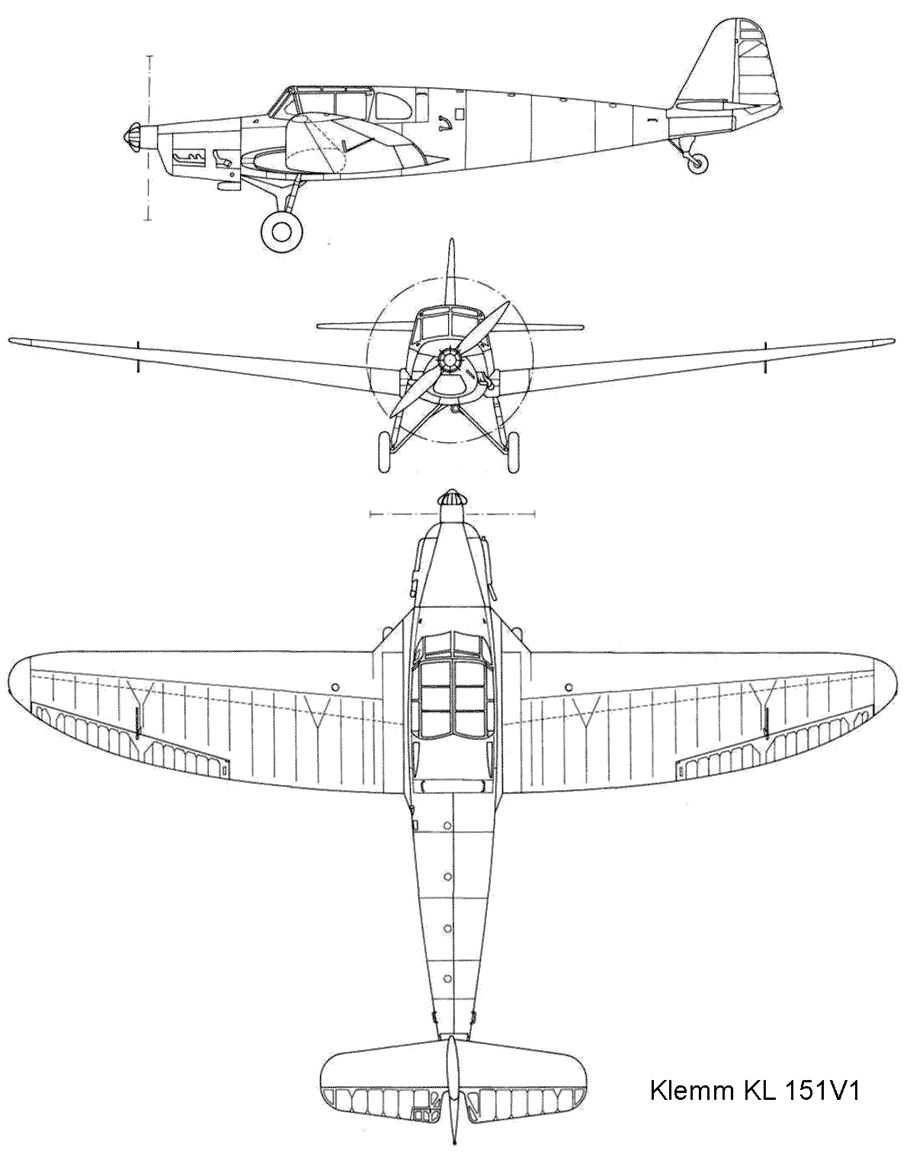 |
Drawing KL 151 V1
|
Bibliography

- Die deutsche Luftrüstung 1933–1945 /Bernard & Graefe Verlag. Heinz J. Nowarra./
- Klemm KL 106 /Luftarchiv.de/
- Historische Deutsche Flugzeuge bis 1945. Klemm KL 106 /Classic Scale./
|





